Redefining IL11 as a regeneration-limiting hepatotoxin and therapeutic target in acetaminophen-induced liver injury | Science Translational Medicine
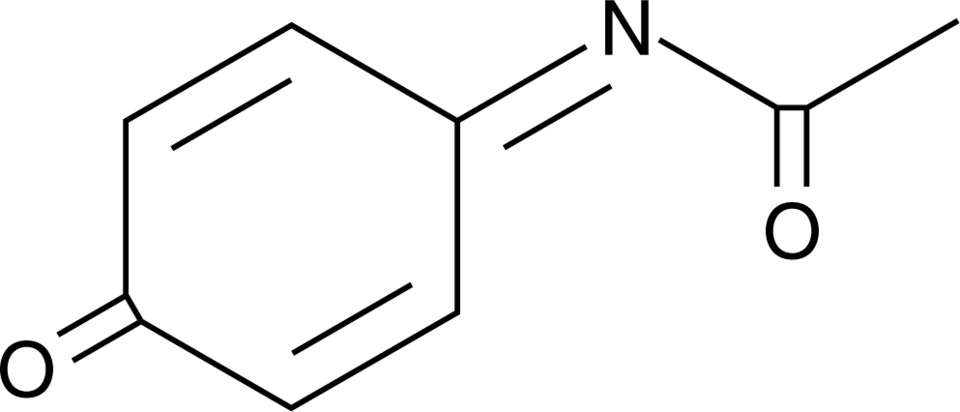
N-Acetyl-4-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI, N-Acetyl-p-benzoquinonimine, CAS Number: 50700-49-7) | Cayman Chemical

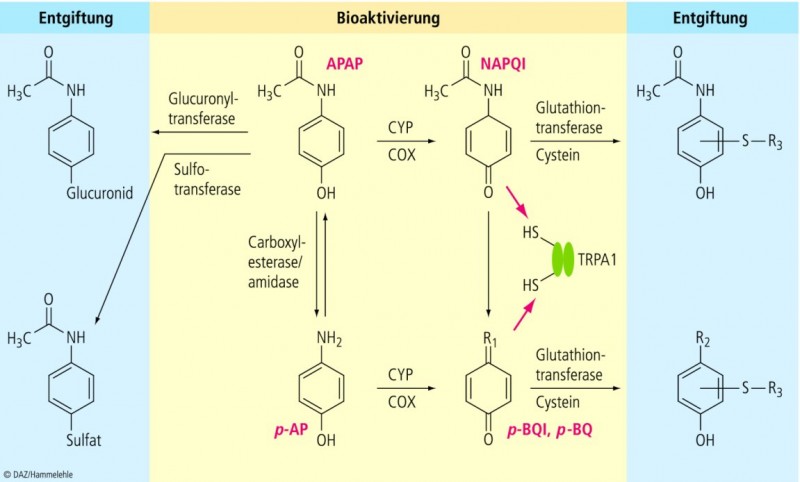
What Are the Potential Sites of Protein Arylation by N-Acetyl-p-benzoquinone Imine (NAPQI)? | Chemical Research in Toxicology
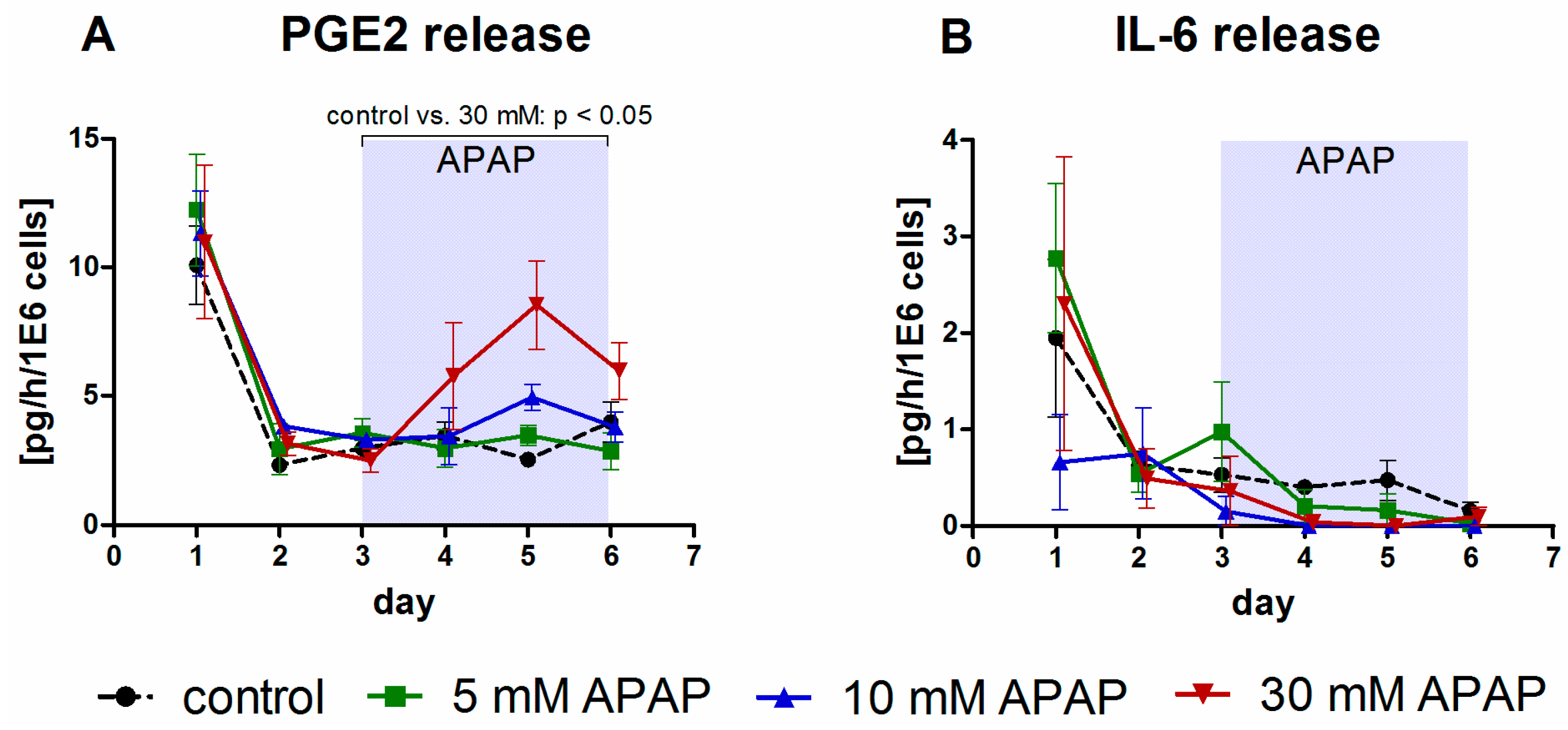
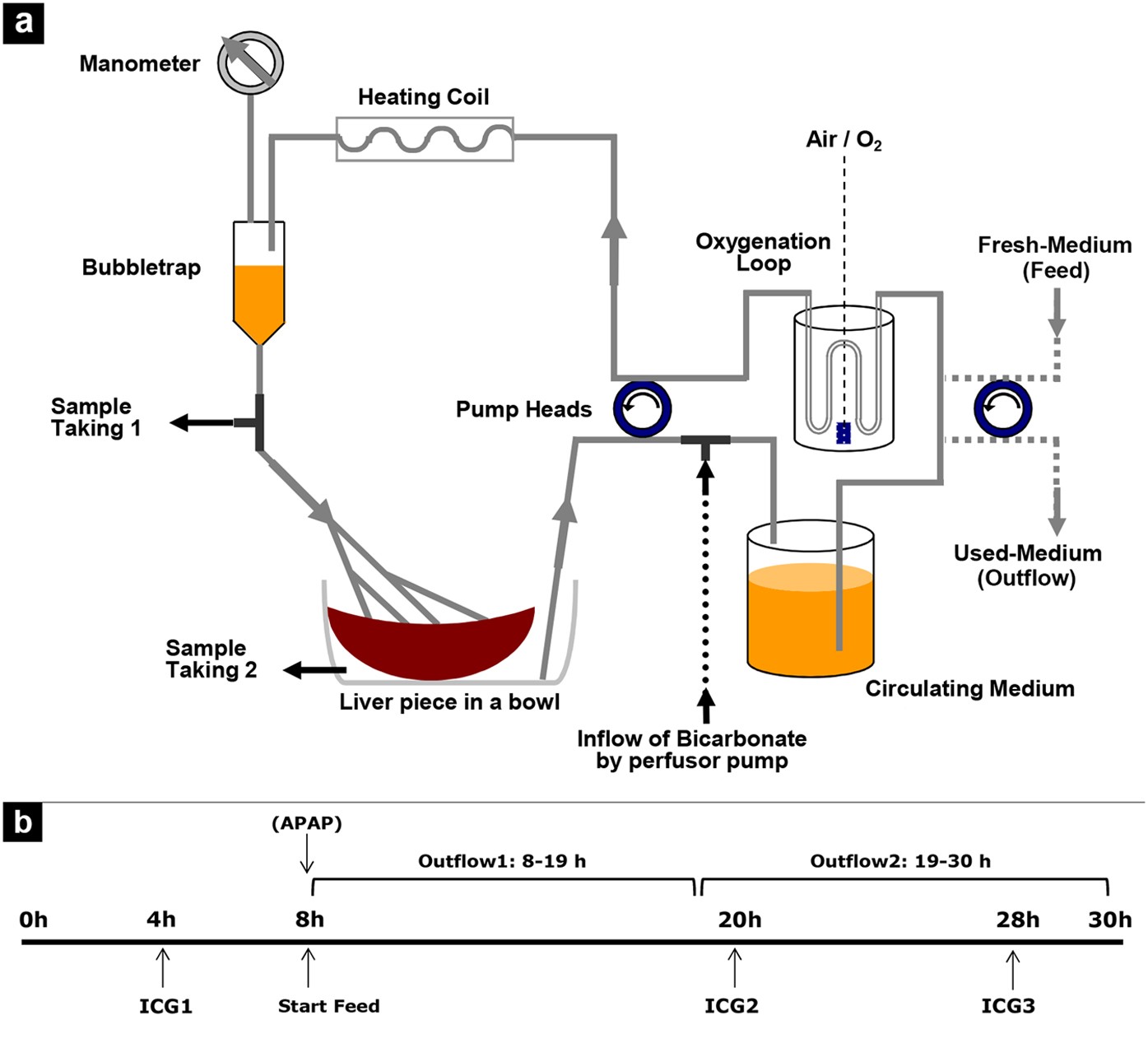
Bioengineering | Free Full-Text | Microscale 3D Liver Bioreactor for In Vitro Hepatotoxicity Testing under Perfusion Conditions

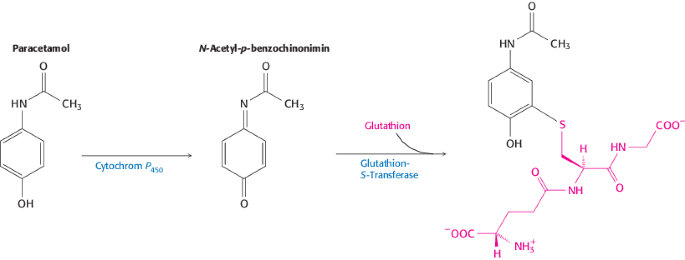
N-Acetyl-p-benzoquinone Imine, the Toxic Metabolite of Acetaminophen, Is a Topoisomerase II Poison | Biochemistry
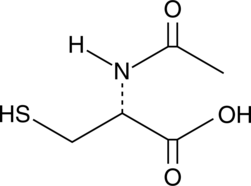
N-Acetyl-4-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI, N-Acetyl-p-benzoquinonimine, CAS Number: 50700-49-7) | Cayman Chemical

N-Acetyl-p-benzoquinone Imine, the Toxic Metabolite of Acetaminophen, Is a Topoisomerase II Poison | Biochemistry

In-source formation of N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI), the putatively toxic acetaminophen (paracetamol) metabolite, after derivatization with pentafluorobenzyl bromide and GC–ECNICI-MS analysis - ScienceDirect
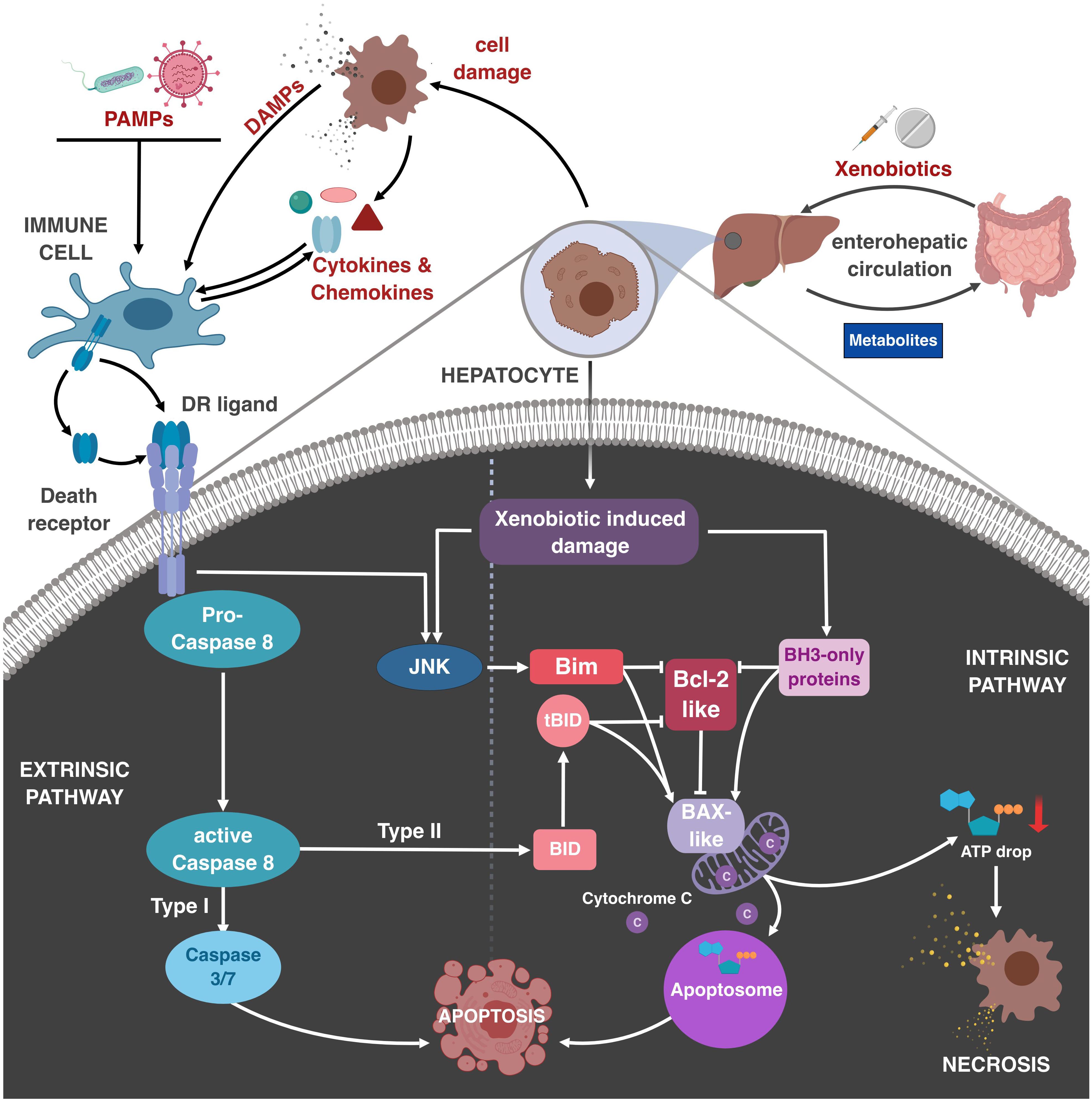
Frontiers | Death Receptor Interactions With the Mitochondrial Cell Death Pathway During Immune Cell-, Drug- and Toxin-Induced Liver Damage
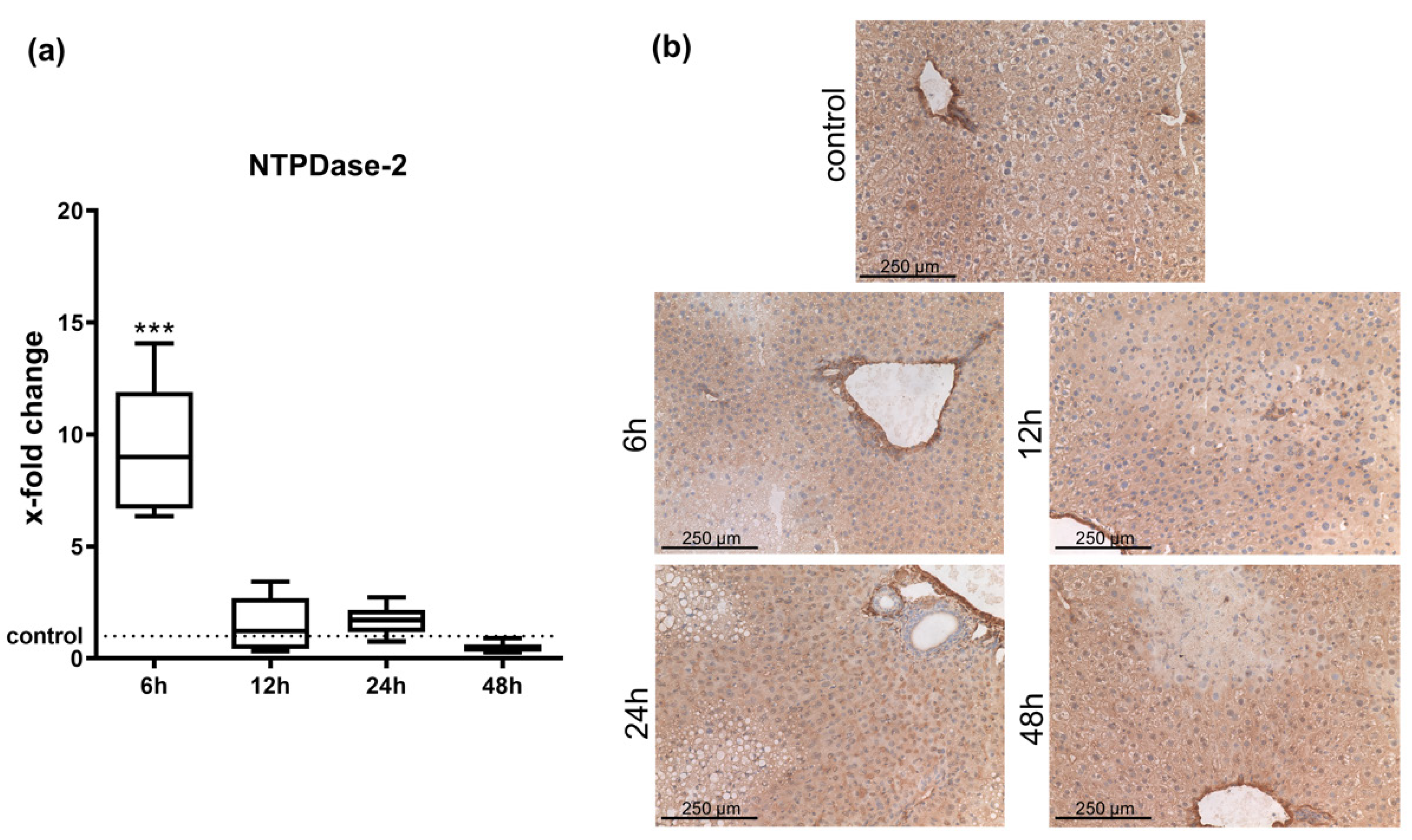
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Ecto-Nucleotide Triphosphate Diphosphohydrolase-2 (NTPDase2) Deletion Increases Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity